Understanding the nuances of compulsory and voluntary excess in motor insurance is essential for you (policyholder), aiming to make informed decisions and optimise your insurance benefits. This comprehensive guide explores the definitions, differences, implications, and strategic considerations associated with these excess types, enabling you to tailor your motor insurance policy effectively.
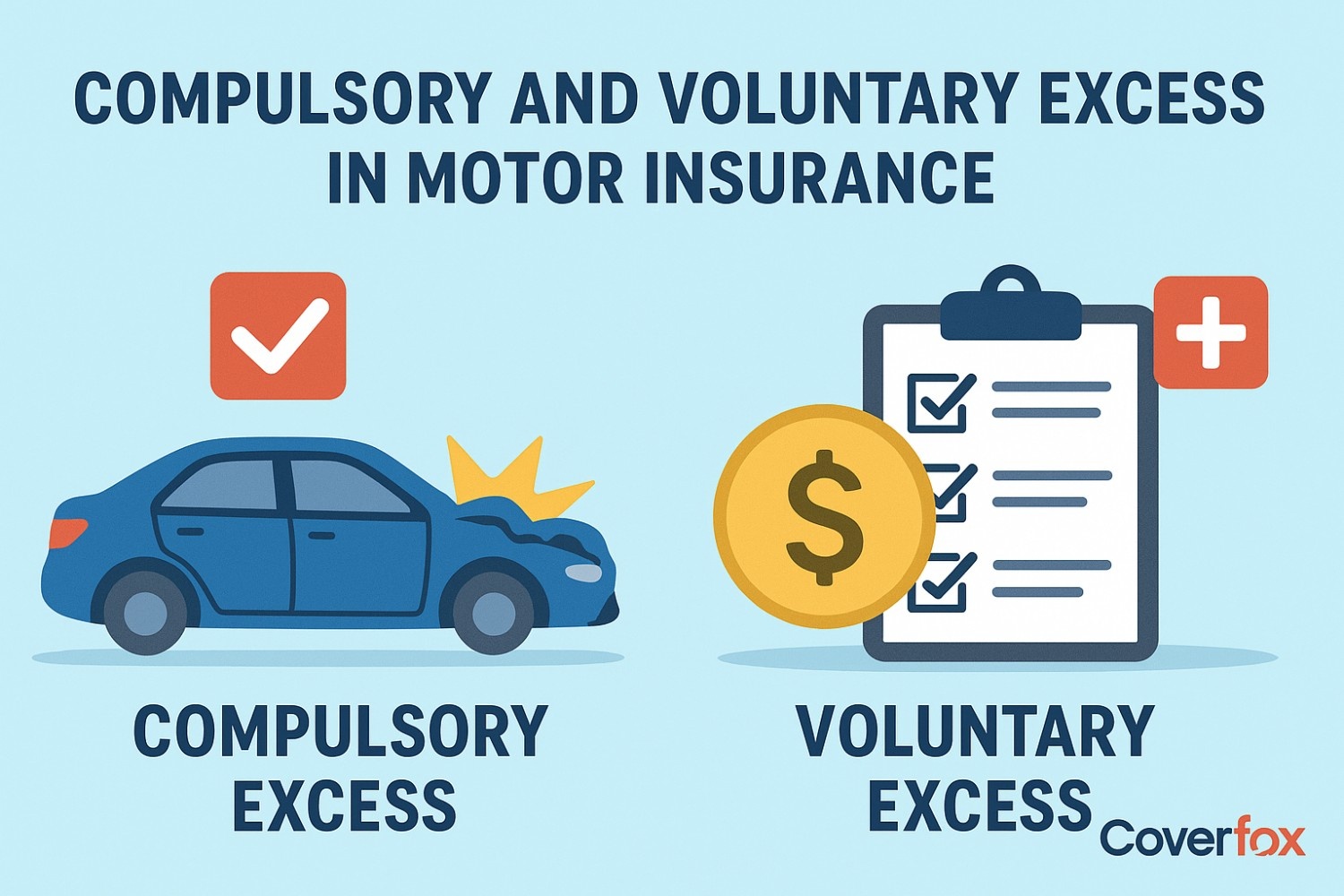
What is Excess in Motor Insurance?
In motor insurance, excess refers to the part of a claim amount that the policyholder agrees to pay out of pocket before the insurer covers the remaining costs. Excess, also called a deductible, is the portion of a claim the policyholder pays before the insurer covers the rest. The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) mandates a compulsory excess for certain vehicles. This ensures policyholders share some risk, discouraging very small claims and keeping the claims process efficient. Excess is primarily categorised into two types: compulsory excess and voluntary excess.
Compulsory Excess
Compulsory excess is a fixed, non-negotiable amount set by insurers under IRDAI regulations. The amount depends on the type of vehicle and engine capacity. It applies uniformly across insurers for private cars and two-wheelers, but may vary for commercial vehicles.
Standard Compulsory Excess Amounts
In motor insurance, there are some costs you always have to pay before you receive the claim. These fixed amounts do not reduce your premiums but ensure that every claim involves some cost-sharing by the policyholder. This system discourages minor claims and helps insurers manage risks better. Being aware of them beforehand helps you handle claims more easily.
| Vehicle Type | Engine Capacity | Compulsory Excess |
|---|---|---|
| Private Cars | Up to 1500 cc | ₹1,000 |
| Private Cars | Above 1500 cc | ₹2,000 |
| Two Wheelers | Up to 150 cc | ₹500 |
| Two Wheelers | Above 150 cc | ₹1,000 |
These are non-negotiable amounts, and hence, the same would be applied uniformly across the industry.
Voluntary Excess
Voluntary deductible is the amount that the policyholder chooses to pay over and above the compulsory excess. Voluntary excess is optional. You can choose to contribute an additional amount beyond the compulsory excess in case of a claim. In return, insurers usually offer a lower premium. The higher the voluntary excess you select, the more your premium may be reduced, though the impact varies by insurer and policy type.
How Does Voluntary Excess Work?
Voluntary excess is an amount you choose to pay yourself in case of a claim, along with the compulsory excess set by the insurer. It impacts your premium at the time of purchase and affects the cost you need to pay during the claim settlement. Here’s how the process of voluntary excess works:
1. Policy Purchase
When you purchase motor insurance, you’re given the option to choose a voluntary excess amount. There is a portion of repair costs you agree to pay from your side in case of a claim, and it becomes a part of your policy terms.
2. Premium Impact
The voluntary excess you choose directly affects your motor insurance cost. Getting a higher excess reduces your premium, while a lower one keeps the premium higher but lessens your share of the claims.
3. Claim Raise
If your car meets with any unexpected accident or suffers damage, then you can file a claim with the insurer. This starts the process of getting financial help for repairs.
4. Excess Applied
During your claim settlement, both the compulsory excess set by the insurer and the voluntary excess you agreed upon are deducted. This ensures that you share the part of the repair cost, lowering your out-of-pocket expenses.
5. Final Payout
After your share is paid, the insurer covers the rest of the expenses. This balance payment helps the policyholder to complete the repair or damage settlement smoothly.
Advantages of Choosing Voluntary Excess
Going for voluntary excess can help the policyholder lower the insurance premium and make the policy more affordable. It encourages you to drive carefully, as you take on a portion of the risk. Overall, it’s a practical way to balance cost and coverage. So, here are some of the key benefits which you can consider:
Lower insurance premiums compared to other standard policies.
Flexibility to choose an excess amount that can fit your budget.
Encourages responsible driving to avoid frequent claims.
It can make motor insurance more affordable for low-risk drivers.
Potential long-term savings if claims are rare.
Disadvantages of a Voluntary Excess
If you opt for a voluntary excess in motor insurance, it can lower your premium, but it also comes with certain risks. Though it may seem cost-effective at first, it later affects your claim payout and financial comfort during unexpected repairs. Here are some key drawbacks to consider:
Higher personal expenses when making a claim
Risk of financial stress during costly repairs
Reduced claim payout if the repair cost is less than the excess amount
Might stop you from filing smaller claims, even if they are valid.
If multiple claims arise, then it can affect overall financial stability.
Key Comparison Between Compulsory and Voluntary Excess
Compulsory and voluntary excess differ mainly in who sets the amount and how it affects your premium. Comparing them helps you understand their impact on claims and overall insurance expenses.
| Area | Compulsory Excess | Voluntary Excess |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Compulsory and decided by the insurer | Voluntary and selected by the policyholder |
| Amount | Pre-set according to the type of vehicle and its engine capacity | Variable; can be increased or decreased at the discretion of the policyholder |
| Effect on Premium | Does not directly affect it | Higher voluntary excess can result in lesser premiums |
| Objective | To get the policyholder involved in claims | To reduce premium costs and discourage minor claims. |
Strategic Considerations for Policyholders
Policyholders should try to balance coverage needs, risk tolerance, and budget while choosing a motor policy. They need to make smart decisions, like selecting excess levels, to help optimise protection and manage premiums. When choosing the voluntary excess amount, you can consider the following points:
- Financial Capability: You should be able to afford the total excess amount, compulsory + voluntary, in case of a claim.
- Driving Habits: If you have a history of safe driving with minimal claims, then a higher voluntary excess may be a good option.
- Vehicle Usage: If the vehicle is occasionally used or only for short distances, a higher voluntary excess may be payable because the probability of claims occurring may be lower.
- Vehicle Age / Value: For older vehicles with lower market value, opting for higher voluntary excess may make sense since claims are likely to be less frequent and lower in payout.
Claims Impact on Excess
When you file a motor insurance claim, the concept of excess directly impacts how much you pay from your own before the insurer contributes. The total excess is the combined amount of compulsory and voluntary excess, which reduces the insurer’s payout but increases your upfront responsibility.
Let’s understand this concept of how claims impact with an example here:
Consider that your car repair bill after an accident comes to ₹20,000. If your policy has a compulsory excess of ₹1,000 and you choose a voluntary excess of ₹2,000, the total excess becomes ₹3,000. This means you must first pay ₹3,000 towards the repair cost, and the insurer will then cover the remaining ₹17,000. As a result, this lowers your premium at the time of purchase but raises the amount you pay during claims, making it a trade-off between immediate savings and future out-of-pocket expenses.
Summing Up
Understanding compulsory and voluntary excess in motor insurance is crucial for policyholders. Knowing how each works helps you make informed decisions, balance premiums with out-of-pocket expenses, and choose the right cover for your financial needs. By understanding compulsory and voluntary excess, policyholders can balance affordability with adequate protection. Comparing car insurance policies online can help you see how different excess levels affect premiums and claims. Coverfox lets you compare multiple insurers and find the right balance of coverage and cost.
Explore More:
Motor Insurance Types in India: Choosing the Right Coverage
Essential Facts about Voluntary Deductible in Car Insurance!
Should you increase the IDV of your car?
Frequently Asked Question
Is it mandatory to have voluntary excess in my car insurance?
No, voluntary excess depends on your choice and mainly helps you to lower your premium.
Is it worth paying voluntary excess?
If you want to lower the premiums and are confident in avoiding small claims, then it's worth paying for it.
How is the compulsory excess determined?
The insurer fixes the compulsory excess based on your policy and the car/bike engine.
Can I modify the voluntary excess?
Yes, you can adjust it according to your condition, but making changes may affect your premium.
What is voluntary excess in vehicle insurance?
Voluntary excess is the extra amount you agree to pay towards a claim to lower your premium.
Does voluntary excess affect my No-Claim Bonus (NCB)?
No, your NCB depends on claim history, not excess selection.