IDV (Insured Declared Value) is not an alien concept in car insurance. If you are preparing to insure your car soon, here's what you ought to know about the IDV and its significance in computing premium.

If you are buying Car Insurance for the very first time or getting your Car Insurance Policy renewed at the end of the policy period, chances are you will get intimidated by the modus operandi undertaken to calculate your car insurance premium.
Well, such an overplay of emotion is quite natural as different types of Car Insurance Policies and the factors impacting the premium calculation could be tad complex. It could eventually make things pretty devastating for you and thereby aggregating your dependency on the insurance provider.
One such concept in Car Insurance is IDV i.e. Insured Declared Value. But before we delve into it further, lets first put some light on the types of Car Insurance Policies.
There are 2 types of Car Insurance Policies for you to avail as a customer.
Third Party Insurance which is mandatory for every vehicle owner to undertake as per the Motor Tariff Act
Comprehensive Insurance Policy.
The Comprehensive Insurance Policy comprises of two covers – Own Damage (OD) and Third Party. OD covers loss or damage to your own vehicle against accidental damage, natural and man-made calamities whereas third-party cover protects the insured against liability due to accidental damages resulting in the permanent injury or death of a third party, and damage caused to the surrounding property.
So where does IDV come in the picture and as a consumer, why do I need to know about it.
What Is IDV?
IDV or Insured Declared Value is the current market value of your vehicle. It is the maximum amount that an insurance company will pay to the insured in case of a claim, that is, in the event of total loss (where the vehicle is no longer capable of running on the road), constructive total loss (when the aggregate cost of retrieval and/or repair of the vehicle is greater than 75% of IDV) or your vehicle being stolen.
Suppose, at the commencement of the policy, if the IDV of your car is fixed for Rs.5 Lacs, then the maximum amount that the Insurance Company will compensate you in the event of total loss, total constructive loss or theft of your vehicle will not be under any circumstances more than Rs.5 Lacs within the policy period.
How Is IDV Calculated?
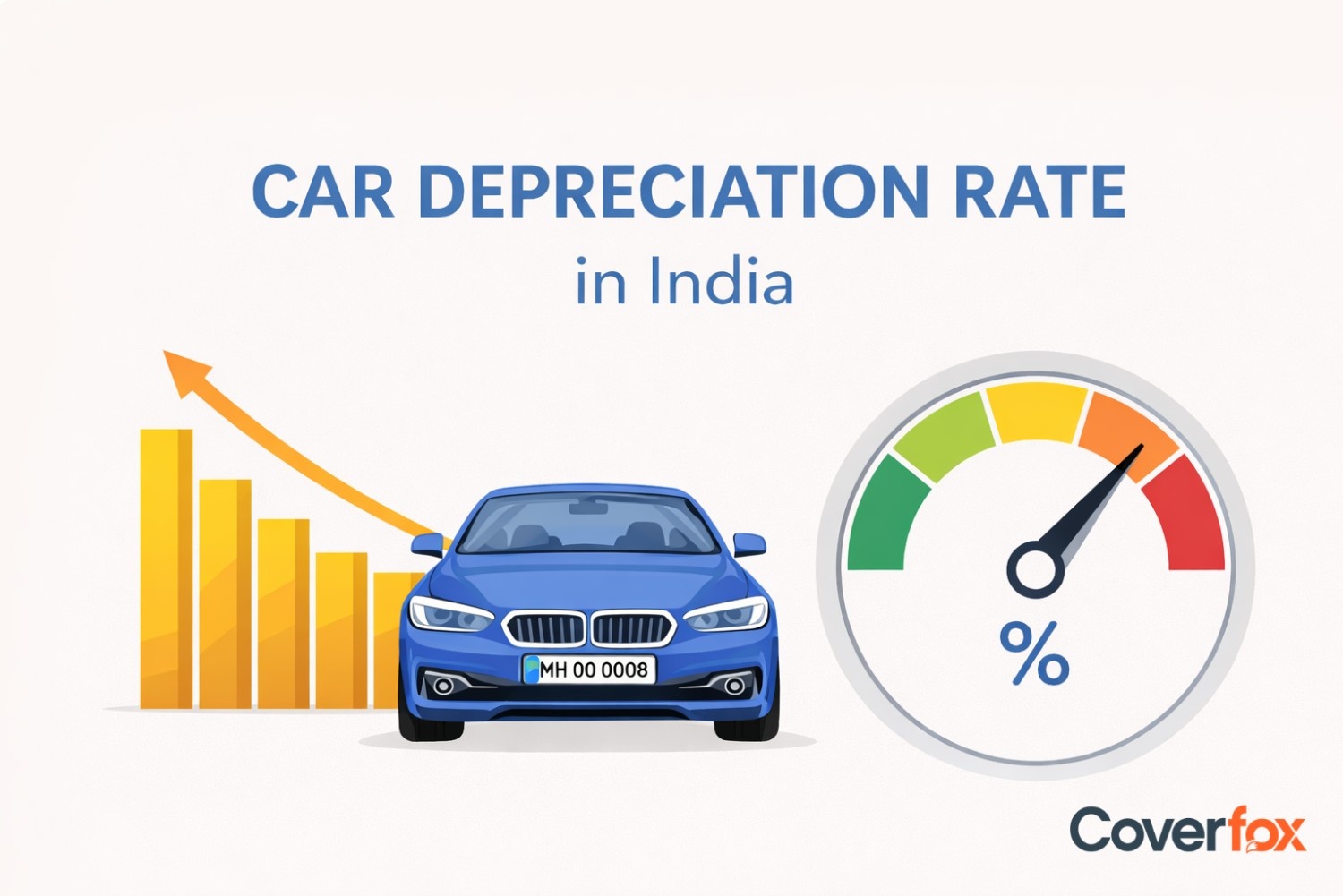
IDV is calculated on the basis of the manufacturer's listed selling price of the brand and the model of the car. Then this amount is adjusted with the standard rates of Depreciation as stipulated by the Motor Tariff Act.
| Age Of The Car | IDV |
|---|---|
| New (0 to 6 Months) | 95% of Ex-Showroom Price |
| 6 Months to 1 Year | 85% |
| 1 Year to 2 Years | 80% |
| 2 Years to 3 Years | 70% |
| 3 Years to 4 Years | 60% |
| 4 Years to 5 Years | 50% |
| 5 Years and Above | Flexible |
It is important for you to understand that at the time of purchase or renewal of your car insurance policy, the insurer considers the current selling price of the brand and the model while computing the IDV for your car and not the price at which you purchased the car.
For instance, if you bought a particular brand and model of car in November 2014 at Rs. 12 Lacs but the price of that same brand and model in January 2016 is Rs. 10.50 Lacs, then the insurer will consider the current listed selling price of Rs. 10.50 Lacs for calculating the IDV of your car.
Also, IDV does not include the cost of registration and insurance. And in case of any accessories that are not factory fitted like speakers or music system, the cost of such items are added to IDV as the value of such items is additional to the price of the car. They are even adjusted for depreciation as these items must have undergone some wear and tear over a period of time.
The formula below summarizes IDV:
IDV = {[(Manufacturer’s listed selling price or Ex-showroom price) + (Sales Tax) + (Accessories that are not included in listed selling price – depreciation)] – (Depreciation + Registration costs + Insurance costs)}
How to Calculate IDV of a vehicle more than 5 year old?
In case of the vehicles that are more than 5 years old or obsolete car models, that is, models of cars which the manufacturers have discontinued to manufacture, the IDV is determined as a result of a mutual understanding between the insurer and the insured.
In such a case, instead of considering the rate of depreciation for calculating IDV, IDV is arrived at by assessing the condition of the car.
Why I Need To Know About The Insured Declared Value Of My Car?
IDV is an important factor while calculating the Own Damage Cover of your car insurance premium under the Comprehensive Insurance Policy. Since the coverage under this policy is comprehensive, covering damages due to accidents, natural disasters and man-made calamities, the OD premium is calculated on the basis of IDV of your car.
Whereas, in case of third party insurance, the premium is computed on the basis of make and model of your car. IDV impacts the OD premium since the rate of depreciation keeps increasing with the increase in the age of the car.
A new car has maximum IDV but as the car ages, the rate of depreciation keeps increasing and resulting in the reduction of IDV. For instance, the car that is less than 6 months old carries a depreciation rate of just 5% whereas a car that is 4 to 5 years old will be charged a depreciation of 50%.
So higher the IDV, higher would be the amount of premium and lower the IDV, lower would be the premium.
What happens when you declare a lower or higher IDV than reasonable Market Value?
Some of us, in the wake of reducing the car insurance premium, declare a lower IDV than the reasonable market value. But we fail to understand that at the time of claim for total loss or theft, we land up receiving a lower claim amount from the insurer since the IDV declared was lower.
In such a case, if there exists total damage or theft of the vehicle, you have to shell out more from your pocket towards the loss as the insurance claim received is quite less. At the same time, if you declare a higher IDV considering that the claim amount will increase in the event of total damage or theft, then it is important for you to note that the insurer will consider the age of the vehicle and hence the rate of depreciation while computing your claim.
You will receive a lower claim amount in the event of total damage or theft despite of the fact that you declared a higher IDV and hence paid higher premium.
Here's an interesting infographic on how to calculate the IDV of your car insurance.

Conclusion
IDV is one of the many factors considered by the insurance providers while calculating your car insurance premium. So if you are buying insurance premium for the first time or getting your auto insurance policy renewed, make sure that the IDV of your car is in accordance with the age and model of your car to avoid any rude shocks during claim.
Also Read: 5 Interesting Facts You Must Know About Car Insurance